Array
11.盛水最多的容器
题目描述
给你 n 个非负整数 a1,a2,...,an,每个数代表坐标中的一个点 (i, ai) 。在坐标内画 n 条垂直线,垂直线 i 的两个端点分别为 (i, ai) 和 (i, 0) 。找出其中的两条线,使得它们与 x 轴共同构成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
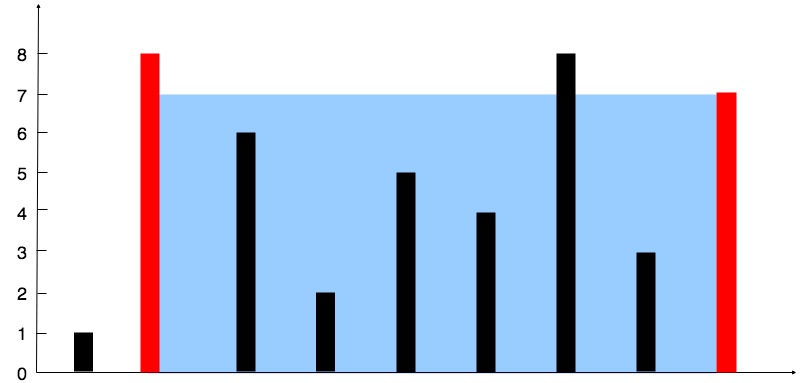
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/container-with-most-water
方法 1:暴力求解
class Solution(object):
def maxArea(self, height):
"""
:type height: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
temp = []
max_value = 0
for i in range(len(height)):
for j in range(i+1,len(height)):
area = min(height[i],height[j]) * abs(i - j)
if area > max_value:
max_value = area
return max_value通过两层 for 循环暴力枚举,时间复杂度是$O(n^2)$,实际提交钟发现会超时。
方法 2:双指针
# 自己写的双指针
class Solution(object):
def maxArea(self, height):
"""
:type height: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
i = 0
j = len(height)-1
res = 0
while i != j:
area = min(height[i],height[j]) * abs(i-j)
if area > res:
res = area
if height[i] > height[j]:
j-=1
else:
i+=1
return res在 LeetCode 的解答里看到了一篇不错的文章,是用来证明双指针法解决这个问题的可行性的,里面也附带了 Python3 的代码,可以看到赋值语句可以借助 Python 的语言特性一行写出来,而不是像我上面那样分三次写,更加优雅。
此外,算法主题部分也有可以学习和借鉴的地方,优化后的双指针写法代码如下。
class Solution(object):
def maxArea(self, height):
"""
:type height: List[int]
:rtype: int
"""
i, j, res = 0, len(height)-1, 0
while i < j:
if height[i]<height[j]:
res = max(res, height[i]*(j-i))
i+=1
else:
res = max(res, height[j]*(j-i))
j-=1
return res参考文章: 盛最多水的容器(双指针法,易懂解析,图解)
283.移动零
题目描述
给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
示例:
输入: [0,1,0,3,12]
输出: [1,3,12,0,0]说明:
- 必须在原数组上操作,不能拷贝额外的数组。
- 尽量减少操作次数。
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/move-zeroes/
方法 1:暴力求解
遍历数组nums,遇到0则删除,并且将其append到数组最后,代码如下,这样做的时间复杂度是$O(n^2)$。
class Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
for i in nums:
if i == 0:
nums.remove(0)
nums.append(0)
return nums值得注意的是,在数组钟进行插入如或者删除操作均会涉及到「群移」,所以在数组钟进行插入或者删除的时间复杂度为$O(n)$。
方法 2
class Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
# 如果数组长度小于1,则无需进行排序,直接返回
if len(nums) <= 1:
return nums
# 用index标记不为0的数的位置
index = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] != 0:
nums[index] = nums[i]
index+=1
# 到这步后index后面的元素都是0
for j in range(index,len(nums)):
nums[j] = 0
return nums
把非零的往前挪,挪完之后剩下的就是零的,补齐即可。这种方法的时间复杂度为$O(n)$,但是需要进行两次遍历操作,可以再想下有没有更好的方法。
方法 3:双指针
class Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
j = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] != 0:
nums[j] = nums[i]
if i != j:
nums[i]=0
j+=1
return numsclass Solution(object):
def moveZeroes(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: None Do not return anything, modify nums in-place instead.
"""
index = 0
for i in range(len(nums)):
if nums[i] != 0:
nums[i] , nums[index] = nums[index], nums[i]
index +=1
return nums70.爬楼梯
题目描述
假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。
每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
注意:给定 n 是一个正整数。
示例 1:
输入: 2
输出: 2
解释: 有两种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 2 阶示例 2:
输入: 3
输出: 3
解释: 有三种方法可以爬到楼顶。
1. 1 阶 + 1 阶 + 1 阶
2. 1 阶 + 2 阶
3. 2 阶 + 1 阶题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/
题目分析
首先可以看到,这道题好像不是那么容易暴力求解的,遇到这种情况就要考虑一下找问题的 最近重复子问题 。
当输入为 1 时,显然输出应该为 1,这是 trival 的。又由上面可知,当输入为 2 时,共有 2 种方法。
再来考虑一下楼梯阶数为 3 时的情况,根据题目示例可以知道共有 3 种情况,如果我们仔细观察可以发现该情况下,爬到楼顶的最后一步只有两种可能,分别是在 1 阶的时候爬 2 个台阶,或是在 2 阶的时爬 1 个台阶,没有其他的可能了。
假设$F$是该阶数下爬到楼顶的方法数,那么我们可以得到以下的关系。
$$ F(1)=1\\ F(2)=2\\ F(3)=F(1)+F(2)\\ \cdots\cdots\\ F(n)=F(n-2)+F(n-1) $$
有没有一种豁然开朗的感觉,没错,这个问题本质上就是一个求解斐波那契数列第 N 个解的问题。
方法 1:递归
class Solution:
@functools.lru_cache(100) # 缓存装饰器
def climbStairs(self, n: int) -> int:
if n == 1: return 1
if n == 2: return 2
return self.climbStairs(n-1) + self.climbStairs(n-2)感觉不超时都难,时间复杂度$O(2^n)$
方法 2:动态规划
class Solution(object):
def climbStairs(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
if n <= 2:
return n
f1,f2,f3 = 1,2,3
for i in range(3,n+1):
f3 = f1 + f2
f1 = f2
f2 = f3
return f3时间复杂度为$O(n)$
方法 3:公式求解
使用斐波那契数列通项公式求解
$$ a_{n}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}\left[\left(\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\right)^{n}-\left(\frac{1-\sqrt{5}}{2}\right)^{n}\right] $$
class Solution(object):
def climbStairs(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: int
"""
import math
sqrt5=5**0.5
fibin=math.pow((1+sqrt5)/2,n+1)-math.pow((1-sqrt5)/2,n+1)
return int(fibin/sqrt5)应该是最快的,时间复杂度为$O(\log{n})$
方法 4:数论解法
此为邪派武功,慎用
class Solution:
def climbStairs(self, x: int) -> int:
return 3267960841*(pow(328501784,x+1,7841400319)-pow(7512898536,x+1,7841400319))%7841400319参考文章:70.重拳出击(Python3)汇集了题解区五大主流方法,要学姿势就要学的全面点
15.三数之和
题目描述
给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
注意:答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [-1,0,1,2,-1,-4]
输出:[[-1,-1,2],[-1,0,1]]示例 2:
输入:nums = []
输出:[]示例 3:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[]题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/3sum
方法 1:暴力求解
使用三层for loop暴力求解出满足条件的三元组,时间复杂度为$O(n^3)$,空间复杂度为$O(1)$
class Solution(object):
def threeSum(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
for j in range(i+1,len(nums)-1):
for k in range(j+1,len(nums)):
if nums[i] + nums[j]+nums[k] ==0:
temp = (nums[i],nums[j],nums[k])
# 排序去重
temp = tuple(sorted(temp))
res.append(temp)
return list(set(res))很轻松地超时了。
方法 2:哈希表
TODO
方法 3:双指针左右夹逼
class Solution(object):
def threeSum(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
# 此算法需要先进行排序
nums.sort()
res,k =[],0
for k in range(len(nums)-2):
# 情况1 因为已经排完序,如果第一个值大于0,那么不可能存在满足题目条件的三元组
if nums[k]>0:
return res
# 情况2 如果k > 0 且 nums[k] = nums[k-1],则跳过nums[k]
# 因为和nums[k-1]的结果是一样的
# 存疑,为什么要k > 0
if k > 0 and nums[k] == nums[k-1]:
continue
# 情况3,双指针求解
i,j = k+1,len(nums)-1
while i < j:
s = nums[k] + nums[i] + nums[j]
if s < 0:
i+=1
while i<j and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:i+=1
elif s>0:
j-=1
while i<j and nums[j] == nums[j+1]:j-=1
else:
res.append([nums[k],nums[i],nums[j]])
i+=1
j-=1
while i < j and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]: i += 1
while i < j and nums[j] == nums[j + 1]: j -= 1
return res参考文章:三数之和(排序+双指针,易懂图解)
本解法时间复杂度为$O(n^2)$,空间复杂度为$O(1)$。

2 条评论
对权力结构的解构充满勇气与智慧。
作者以非凡的视角解读平凡,让文字焕发出别样的光彩。